Marine and offshore
In the 1960s, Danish ship owner A.P. Møller´s bitter experience was that the cargo pumps of his tankers were breaking down far too often, without forewarning. An inventor and an enterprising financier decided to do something about it. The SPM method was invented and since then SPM has been present in the maritime industry.
Also in the early seventies, the entire fleet of British Petroleum tankers, at that time some 80 vessels, were equipped with shock pulse meters for detecting damaged rolling element bearings before they failed. Today, our condition monitoring instrumentation is installed on board more than a thousand vessels.
The maintenance on board vessels has traditionally been based on equipment running time. High demands on the environment, reliability and ship safety have made condition monitoring widely accepted also by classification societies and it is already an option for most vessels. Knowing the condition of your machinery is crucial to avoid sudden failures and maximize equipment lifetime. Timely failure prediction and detection are vital for reducing manpower and spare part inventory to increase profit.
 “We were looking for a supplier who could solve the specialized problems of our clients regarding slow turning machinery. We also wanted a software platform that was ‘analysis friendly. But the most principal factor in our decision to buy the Leonova Diamond was the HD technology."
“We were looking for a supplier who could solve the specialized problems of our clients regarding slow turning machinery. We also wanted a software platform that was ‘analysis friendly. But the most principal factor in our decision to buy the Leonova Diamond was the HD technology."
Bárður Heinason, Machine technician, MEST, Faroe Islands


Solutions for the marine and offshore industries
Since our beginnings, we have continuously developed our product range to include portable instruments, online systems and accessories specifically suited for shock pulse monitoring of important rotating machines on board, like pumps, fans, turbochargers, azipods, electrical motors etc. Vibration monitoring equipment is used on applications where other problems such as alignment, impeller problems, gear problems, balancing problems etc. occur. On slowly rotating machinery, the SPM HD® measuring technique can be used with benefit. SPM HD uses RPM based sampling frequency and algorithmic correlation techniques to ensure the highest possible signal quality and razor-sharp spectrums for analysis.
Portable instruments
Intellinova online systems
HD technologies
Transducers and transmitters
Certified for the marine and offshore industry
CBM in the maritime industry
The trend leans towards larger vessels operated by less crew. Operating large ships with a relatively small crew puts focus on how to use man-hours more effectively. We can learn from Condition Based Maintenance (CBM) strategies implemented by the land-based industry exposed to international competition and adopt this way of working to the maritime industry. A big part of the maintenance work onboard vessels is, in fact, unnecessary and a product of tradition and previous demands by the class.
The combination of unskilled labour and inspections by classification societies of machines stripped for visual inspections have contributed to the extreme workload in many machine rooms. The redundant machines are installed for safety but are mainly used to compensate for the problems this maintenance approach gives.
CBM are routine measurements and inspections carried out by a selected crew trained to evaluate the results and determine possible corrective maintenance. The redundant equipment is included in the inspection to ensure that they work when needed for safety reasons. The CM software can be connected to the maintenance management system to issue work orders and get the action reported back into the system automatically. The machines are prepared with adapters and transducers for ensuring quality readings. Critical equipment like turbochargers can be equipped with online systems for extra protection.
The condition information is used to get an early warning for replacing parts before failure. The readings can also be used for class inspection as an alternative to opening up machines for inspections.
CBM increases reliability, requires fewer man-hours by eliminating unnecessary maintenance caused by time-based inspections and the extra work that catastrophic failures give. The work can be planned and give the crew stable working hours. In addition, there is a reduction in spare part consumption allowing a smaller stock and making the number crunchers happy.

Application example: Turbo charger
Our solution
Shock pulse transducers installed in the bearing housings, both on the turbine and the compressor side, are connected by coaxial cables to a multichannel measuring and display module. A vibration transducer monitors the overall movement. The readings can also be captured with a handheld unit, e.g. Leonova Diamond or Leonova Emerald. You get an instant, user-friendly condition evaluation on a green-yellow-red scale. The system gives immediate results as maximized up-time, increased profitability and reduced cost etc.
The concept of air compression and expansion has been used in a variety of applications: gas turbines, steam turbines, wind energy, turbo charging of diesel engines and is commonly used in the maritime industry.
A turbo charger comprises a turbine and a compressor connected by a common shaft, supported on a bearing system.
The turbo charger converts waste energy into compressed air which it pushes into the engine. This allows the engine to produce more power and torque and improves the overall efficiency of the combustion process.
The turbo charger has two bearings, one on the compressor side and one on the turbine side. The bearings are either of roller bearing type or sleeve bearing type.
A breakdown of a turbo charger is very costly. Direct costs are primary and secondary material damages. Indirect costs are off-hire of the ship, penalties due to late arrival to port because of decreased speed, badwill in front of passengers etc. Therefore, condition monitoring of turbo chargers is very important when it comes to monitoring the condition of the turbo charger and planning its maintenance to eliminate any unplanned stops.
Typical faults and trends
While in good condition, turbo charger bearings produce very stable shock pulse readings. Due to the high rpm, the fatigue of these bearings results in a fairly rapid damage development. A few weeks´ warning time can be expected, but it is advisable to replace the bearing at the first opportunity after an increase in the shock level. Vibration above all increases on the turbine side when the compressor is fouled and needs cleaning. Combustion residues on nozzle vanes and turbine blades cause a considerable drop in compressor efficiency.
Bearing damage
The bearing can be damaged due to normal wear, poor lubrication oil, incorrect mounting etc. If the turbo charger runs until the bearing breaks down due to any of the above reasons this will cause the turbo charger to stop and the bearing will have to be replaced before startup. Bearing damage might also cause secondary damages to the turbine and to the compressor.
Rotor imbalance
Rotor imbalance means that the turbo charger starts to vibrate. This is because the blades have dirt deposit causing these vibrations. If the turbo charger is run towards a rotor breakdown this will cause the turbo charger to stop. The rotor will have to be replaced and most probably secondary damages will have to be fixed.
The solution
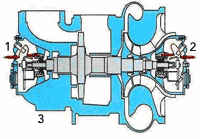
1) Turbine bearing 2) Blower bearing 3) Turbine vibration
A breakdown is very costly, mainly due to material costs. The time from worsened condition to a breakdown is much shorter compared to many other applications, due to the very high speed at which turbo chargers are run. An online solution is therefore often preferred when monitoring the condition of turbo chargers.
Suggested methods
Roller bearing types
SPM monitoring of the bearings with the SPM® method. Vibration monitoring on the housing for measuring the impeller condition.
Sleeve bearing types
Vibration monitoring
For trending and alarm handling, SPM Instrument supplies units which give 4-20 mA output for connecting to local PLC. A solution with the Condmaster® Ruby software can also be implemented.








